This length converter is a tool that enables quick conversion between length units in both imperial and metric, but not only that. It's equipped with twenty different units of length measurement:
- ångström (Å)
- picometers (pm)
- nanometers (nm)
- micrometers (μm)
- millimeters (mm)
- centimeters (cm)
- decimeters (dm)
- meters (m)
- meters and centimeters
- kilometers (km)
- thousandths of an inch (mil / thou)
- inches (in)
- feet (ft)
- feet and inches
- yards (yd)
- miles (mi)
- nautical miles (nmi)
- Sun radii (R☉)
- light years (ly)
- astronomical units (au)
- parsecs (pc)
This length conversion calculator works by typing units (up to 11 in the same calculation) into the tool. The length converter then returns your results in each unit in real time. Click on the unit name if you want to perform length conversion to a different unit than the default ones chosen by the Omni team.
Once you've mastered lengths and their conversion, you can apply that knowledge to circles in our circle length calculator. If you are looking to convert between units of area, another tool we would recommend is the square footage calculator.
Length conversion table
To find out what the conversion factors are between nine popular length units, check out this length conversion table:
millimeter (mm) | centimeter (cm) | meter (m) | kilometer (km) | inch (in) | foot / feet (ft) | yard (yd) | mile (mi) | nautical mile (nmi) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 millimeter (mm) | 1 | 0.1 | 0.001 | 0.000001 | 0.03937 | 0.003281 | 0.0010936 | 0.0000006214 | 0.00000054 |
1 centimeter (cm) | 10 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.00001 | 0.3937 | 0.03281 | 0.010936 | 0.000006214 | 0.0000054 |
1 meter (m) | 1000 | 100 | 1 | 0.001 | 39.37 | 3.281 | 1.0936 | 0.0006214 | 0.00054 |
1 kilometer (km) | 1000000 | 100000 | 1000 | 1 | 39370 | 3281 | 1093.6 | 0.6214 | 0.54 |
1 inch (in) | 25.4 | 2.54 | 0.0254 | 0.0000254 | 1 | 0.08333 | 0.02778 | 0.000015783 | 0.000013715 |
1 foot / feet (ft) | 304.8 | 30.48 | 0.3048 | 0.0003048 | 12 | 1 | 0.33333 | 0.0001894 | 0.00016458 |
1 yard (yd) | 914.4 | 91.44 | 0.9144 | 0.0009144 | 36 | 3 | 1 | 0.0005682 | 0.0004937 |
1 mile (mi) | 1609344 | 160934 | 1609.3 | 1.6093 | 63360 | 5280 | 1760 | 1 | 0.869 |
1 nautical mile (nmi) | 1852000 | 185200 | 1852 | 1.852 | 72913 | 6076 | 2025.4 | 1.1508 | 1 |
We've decided to round some of the conversion factors to fit into this table. Thus, some of these values are not exact, but they still have reasonable accuracy.
Length conversion chart
If you are wondering how to quickly convert between different units from the same system, check out these two simple length conversion charts:
- Metric measurement system

As an example:
- 6 km = 6 × 1000 = 6000 m
- 180 cm = 180 / 100 = 1.8 m
- Imperial / US measurement system

For instance:
- 5 yd = 5 × 3 = 15 ft
- 144 in = 144 / 12 = 12 ft
Moreover, we've decided to make a list of the most popular length conversions. The ones that you're often asking for are:
-
meters to feet / feet to meters
If you're wondering how many feet there are in a meter, here you are:
1 meter ≈ 3.281 feet, which is 3 feet 3⅜ inches1 foot = 0.3048 meter
-
cm to inches / inches to cm
Find out how many centimeters are in an inch:
1 centimeter ≈ 0.3937 inches1 inch = 2.54 centimeters
-
feet to inches / inches to feet
To convert between inches and feet use:
1 foot = 12 inches1 inch ≈ 0.08333 feet1/12 of a foot
-
feet to yards / yards to feet
How many feet in a yard? Three!
1 yard = 3 feet1 foot ≈ 0.3333 yards, 1/3 of a yard
-
feet to miles / miles to feet
Have you ever wondered how many feet there are in a mile?
1 foot ≈ 0.00018939 mile1 mile = 5280 feet
Inch definition

The inch (abbreviate as in or ") is a unit of length in Imperial / the US system. The measure comes from - by some definitions - the width of a human thumb. In some languages, e.g. Norwegian, Afrikaans, Italian or French, an inch is derived from the word for thumb or, in some cases, it's the same word. In the 14th century, the inch was defined by the king of England as three grains of barley, dry and round, placed end to end, lengthwise.
Inch definition varied through the ages but during the 1950's an international standard was accepted, and since then the inch is equal to exactly 2.54 centimeters.
1 in = 2.54 cm
One inch is also equal to 1⁄36 yard, 1⁄12 of a foot or 1⁄63360 of a mile.
On a daily basis, inches are used in US, UK, Canada and other countries which were formerly part of the British Empire. Height, length, width may be measured in inches, also many sizes are expressed in units derived from inches (e.g. shoe size).
What can be measured in inches - not only in the US, but worldwide?
- screen sizes of smartphones, monitors, TVs, (specifically, the diagonals of rectangular screens)
- screen resolution in pixels per inch (for more information, head to our ppi calculator)
- tire sizes - e.g. car or bike wheels,
- different tools and pipes sizes
- some sport equipment uses the values in inches e.g. for archery
One international inch is then equal to:
- 10,000 tenths
- 1,000 thou / mil
- 100 points or gries
- 72 PostScript points
- 6 computer picas
- 3 barleycorns
- 2.54 centimeters exactly
- 0.999998 US Survey inches
- 1/3 or 0.333 palms
- 1/4 or 0.25 hands
- 1/12 or 0.08333 feet
- 1/36 or 0.02777 yards
Feet definition
The foot (abbreviate as ft or ') is a unit of length in an Imperial / US system. It's a measurement based on the human body as well, as the name indicates. The unit was standardized in the 1950s, and since then it's equal to 0.3048 meters exactly:
1 ft = 0.3048 m = 304.8 mm
The use of feet has been around since ancient times by many different civilizations, but the actual length differed between them. The foot was used, e.g. in:
- Ancient Rome: 1 foot = 11.6 inches (295.7 mm). That was a standard foot, but in some provinces it could be as much as 13.2 inches (334 mm)
- Greece: 1 foot = 10.6-13.8 inches (270 - 350 mm)
- Indus cities during the Bronze Age: 1 foot = 13.2 inches (333.5 mm)
- Egypt, the foot equivalent = 12 inches (304.8 mm)

In England, the foot measure also changed through the ages - it started from Roman standards, then Belgic Celts foot of 13.2 inches or Welsh foot came and went. The feet definition varied from region to region, city to city, later even the kings changed the measure according to their desire - e.g., Henry I was said to have ordered a new standard based upon his arm. Then Edward II of England introduced some kind of standardization by introducing the statute foot which was 10⁄11 of the old foot. The final agreement on the foot length came much later, in 1959, when the was accepted. Since then, yard in the United States and countries in the British Commonwealth is equal to exactly 0.9144 meters. As yard was defined, the foot could be calculated as well. Thus, it's equal to:
1 foot = (1/3) × yard = (1/3) × 0.9144 m = 0.3048 m
In the US, two types of feet are used: the international foot and the survey foot:
-
International foot
Also named the standard foot; it's the one standardized in the 1950s. Used widely in many applications, it's equal to 0.3048 m:
1 international foot ≡ 0.3048 m, where we used the≡sign to emphasize it's equal to exactly this valueThe international foot measure corresponds to a human foot with a shoe size of 13 (UK) or 14 (US male).
-
Survey foot
The US survey foot is almost identical in measure to the international foot. But the word almost is the key - the survey foot definition is precisely 1200/3937 meters:
1 US survey foot = 1200/3937 m ≈ 0,30480060960121920243840487680975... mAs you can see, it looks like a really tiny difference - something changes at the seventh decimal place! Which is a difference of ≈0,609 μm ≈ 609 nm, comparing the one type of a foot to another. Why do we even care?
It's important because the difference is negligible if we measure relatively small objects, but it grows significantly if we begin measuring hundreds of thousands of feet, as in mapping or using state plane coordinate system (SPCS). Furthermore, the legislation on the survey foot varies between the 50 states:
-
24 states have legislated that surveying measures should be based on the US survey foot
-
8 states have decided that it should be made on the basis of the international foot
-
18 states haven't specified the conversion factor from metric units
-
The National Institute of Standards and Technology has deprecated the survey foot "except for historic and legacy applications".
But don't worry too much - if you need the conversion for your everyday land surveying or real estate transactions, the difference is really negligible for short distances (< 1 mile), so it doesn't matter which definition you settle on.
There's one other foot measurement - the Indian survey foot. It's defined as exactly 0.3047996 m:
1 Indian survey foot = 0.3047996 m -
Feet - and the whole imperial system - are used widely in the US. And almost only there. The US is the only industrialized country in the world that hasn't officially adopted the International System of Units, also called the metric system. The other two countries using the imperial system are Liberia in Africa and Myanmar (also known as Burma) in Southeast Asia. Canadians and the British use a mix of both systems - metric and imperial (e.g. men's height is usually expressed in feet combined with inches).
Feet are not widely used outside of the English-speaking world. The only obvious example is the measurement of altitude in international aviation.
Meter definition
Meter (British English: metre) is the base unit of length in some metric systems, including the International System of Units (SI).
The meter definition changed as scientific methods in measuring developed. Now it's defined as the length of the path traveled by light in a vacuum in 1/299,792,458 of a second.
But how was it characterized before?
- First trials to create the meter definition started in 1790. At that time, The French National Assembly decided that the length of a new meter would be equal to the length of a pendulum with a half-period of one second. You can check out how accurate this measure was with our simple pendulum calculator. Type 2 in the pendulum period box and you'll obtain the pendulum length value. Indeed, it's really close to the one meter (0.993621 m).

-
In 1973, the circumference of the Earth was chosen as a neutral standard. The meter was defined as one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator to the North Pole:
1 meter = 1/10,000,000 the quarter meridional circumference of the Earth, along the Earth's meridian through Paris -
1799 - 1889, brass, platinum, and the alloy of platinum with 10% iridium meter bars were constructed, still as a basis having Earth's meridian length. The 1st General Conference on Weights and Measures in 1889 defined the meter as the distance between two lines on a standard bar of the latter type of alloy. This International Prototype Meter is still kept in the International Bureau of Weights and Measures in Sèvres, near Paris. That meter definition was in force till 1960 and the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures.
-
From 1960 to 1983 the meter was redefined once again as 1,650,763.73 wavelengths of the orange-red radiation of krypton 86 under specified conditions.
-
17th Conference defined the meter as 1/299,792,458 of the distance light travels in a vacuum in one second, and this meter definition is actual to this day.
The table below sums up the chronology of a meter definition .
Standard | Date | Absolute error | Relative uncertainty |
|---|---|---|---|
1/10,000,000 of the quadrant along the meridian | 1795 | 500–100 μm | 10−4 |
First prototype of platinum bar standard | 1799 | 50–10 μm | 10−5 |
Platinum-iridium bar at melting point of ice (1st CGPM) | 1889 | 200–100 nm | 10−7 |
Platinum-iridium bar at melting point of ice, atmospheric pressure, supported by two rollers (7th CGPM) | 1927 | n.a. | n.a. |
Hyperfine atomic transition; 1650763.73 wavelengths of light from a specified transition in krypton-86 (11th CGPM) | 1960 | 4 nm | 4×10−9 |
Length of the path traveled by light in a vacuum in 1/299 792 458 second (17th CGPM) | 1983 | 0.1 nm | 10−10 |
Imperial / US measurement system
Imperial and US measurement system are not the same thing, but for length measures they are the same (they are non-identical in volume measures, so e.g. the cup can contain different amount of fl oz from both systems). The only countries which didn't accept the metric units are US, Liberia and Myanmar.
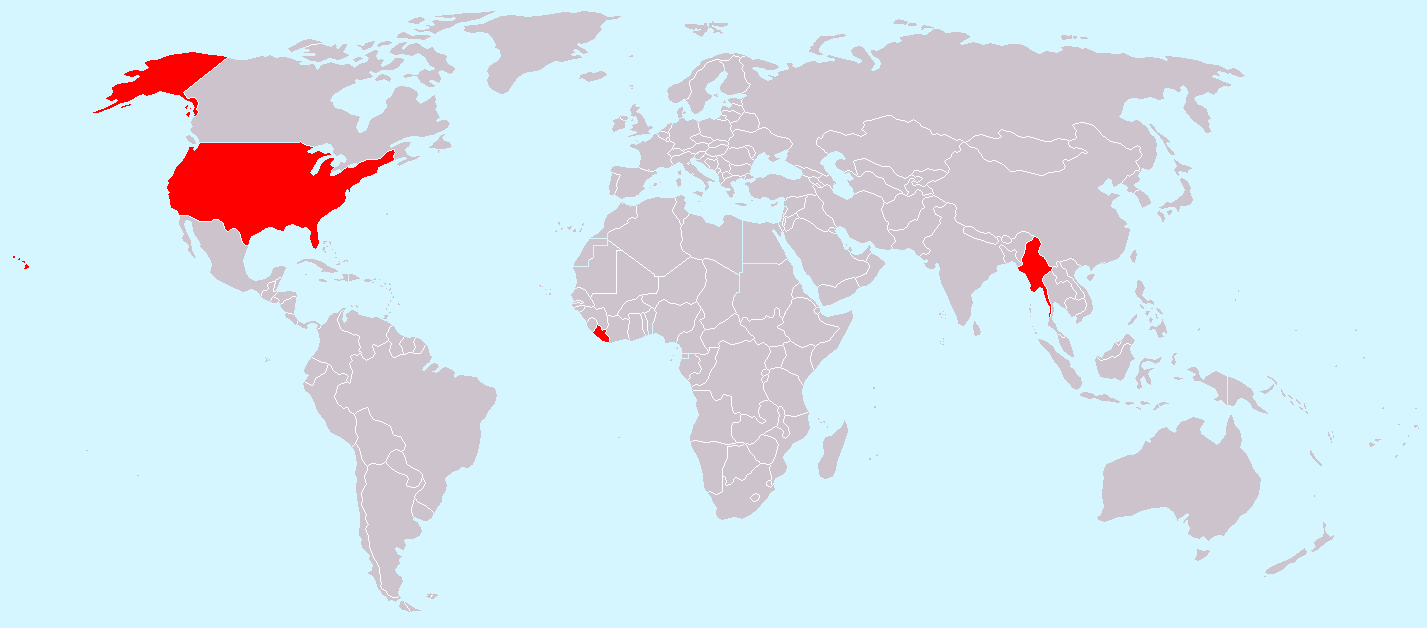
Six most often used US / imperial length units were put into our length converter:
- thousandth of an inch (mil / thou),
- inches (in),
- feet (ft),
- feet and inches,
- yards (yd),
- miles (mi).
There are two other length units, but we excluded them from this length converter on purpose: a furlong's conversion ratio is not uniformly defined, and a league used to be a popular measure in Europe and Latin America but is no longer an official unit anywhere. However, you can find them below, with the most often used values:
Unit | Relative to previous | Feet | Millimeters | Meters |
|---|---|---|---|---|
thou (th) | 1⁄12000 | 0.0254 | 0.0000254 | |
inch (in) | 1000 thou | 1⁄12 | 25.4 | 0.0254 |
foot (ft) | 12 inches | 1 | 304.8 | 0.3048 |
yard (yd) | 3 feet | 3 | 914.4 | 0.9144 |
chain (ch) | 22 yards | 66 | 20116.8 | 20.1168 |
furlong (fur) | 10 chains | 660 | 201168 | 201.168 |
mile (mi) | 8 furlongs | 5280 | 1609344 | 1609.344 |
league (lea) | 3 miles | 15840 | 4828032 | 4828.032 |
Metric measurement system
The metric measurement system, also known as the International System of Units (SI), is an international decimal system of weights and measures. It is used all over the world (apart from three countries mentioned before), it's easy to use, logical and convenient.
Four base units of metric measurement system are:
- meter (m) for length,
- kilogram (kg) for mass,
- second (s) for time,
- ampere (A) for electromagnetism.
Besides, 22 derived units with special names exist. We can split them into 5 categories:
- Electromagnetism
- volt, a unit of electrical potential,
- ohm, a unit of electrical resistance,
- tesla, a unit of magnetic flux density,
- weber, a unit of magnetic flux,
- farad, a unit of electrical capacitance,
- henry, a unit of electrical inductance,
- siemens, a unit of electrical conductance,
- coulomb, a unit of electrical charge.
- Mechanics
- watt, a unit of mechanical or electrical power,
- newton, a unit of mechanical force,
- joule, a unit of mechanical, electrical or thermodynamic energy,
- pascal, a unit of pressure.
- Electromagnetic radiation
- becquerel, a unit of radioactive decay,
- sievert, a unit of absorbed ionising radiation,
- gray, a unit of ionizing radiation,
- lux, a unit of luminous flux,
- lumen, a unit of luminous intensity.
- Circular arcs and spherical surfaces
- radian, a unit of circular arc,
- steradian, a unit of spherical surface area.
- Other
- kelvin, a unit of thermodynamic temperature. Check out this temperature converter to change the degree Celsius into Kelvins or Fahrenheit;
- katal, a unit of catalytic activity,
- hertz, a unit of cycles per second.
FAQs
How do I convert mph to ft?
To convert mph to ft:
- Know that one mile equals 5,280 ft.
- Multiply the number of miles by how many feet there are in one mile.
- As an easy formula:
speed [ftph] = speed [mph] × 5,280
How do I convert metric units of length?
Converting metric units of length:
- 1 mm = 0.1 cm = 0.001 m = 0.000001 km.
- 1 cm = 10 mm = 0.01 m = 0.00001 km.
- 1 m = 1,000 mm = 100 cm = 0.001 km.
- 1 km = 1,000,000 mm = 100,000 cm = 1,000 m.
How do I convert 36 yds to centimeters?
36 yd = 3,292 cm. To convert 36 yds to cm:
- Know that one yard equals 91.44 centimeters.
- Multiply the number of yards by how many centimeters there are in one yard.
length [centimeters] = length [yards] × 91.44length [centimeters] = 36 × 91.44 = 3,292 cm
How do I convert inches length of fabric into centimeters?
To convert inches of fabric to centimeters of fabric:
- There is 2.54 cm in one inch.
- To convert length in inches to length in centimeters, multiply the number of inches by 2.54 (because in every inch, we've got 2.54 cm).
length [cm] = length [in] × 2.54